The National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) has released its annual ‘Cyber Security Breaches Survey’.
The survey is used to inform government policy on digital security, educate British businesses, and ensure UK cyber space remains safe.
Data collected across over 2,400 business and 850 charities produced some startling statistics concerning the ever-looming threat of cyber-attacks infiltrating UK businesses’ digital footprint.
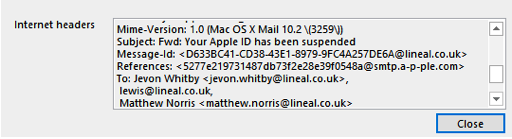
The report discovered that 39% of UK businesses detected an incoming cyber-attack during 2021. Phishing attacks made up a fifth of all threats identified – the most frequent type of malicious attack.
Organisations also revealed that ransomware was being recognised as a serious digital threat with 56% of businesses stating they have installed or will be introducing a company policy to not pay ransoms to cyber criminals.
Whilst 58% of small and medium businesses disclosed to outsourcing their IT Support service, only 23% of surveyed businesses had a cybersecurity incident management strategy in place that is more advanced than a basic endpoint antivirus.
NCSC promote a blend of regular cyber security learning and training processes within your business to better inform the deployment of traditional cybersecurity software measures across all the organisation’s IT systems.
This multi-layered approach aims to counteract the report’s discovery that a lack of cyber technical expertise amongst UK businesses is to blame for threats going undetected.
Similarly, a company-wide policy of digital hygiene erodes the false assumption that managed cybersecurity strategies are a cost to the business rather than a strategic, protective investment.
31% of business admitted being attacked at least once a week showing that any weak link in an organisation’s cyber defence can have grievous financial implications.
To mitigate this, we recommend organisations follow the NCSC’s guidance and adopt Cyber Essentials and Cyber Essentials +. The scheme requires businesses to meet or exceed an assured set of security requirements each year to protect against common forms of online crime, technology dangers and digital threats.
It is estimated that a Cyber Essentials certification can reduce your organisation’s risk of a cyberattack by 98.5% – contact Lineal to assist with your organisation’s application and to help you meet the requirements for a successful certification or re-certification today.