Each year new cyber threats appear to circulate online, and 2023 has certainly been no exception. For cyber criminals, it’s business as usual… right?
Not quite. Over time certain new patterns emerge that are important for cyber security researchers to identify, and these can help protect businesses and organisations in the future. So what can we learn from this year’s crop of nasty ransomware strains?
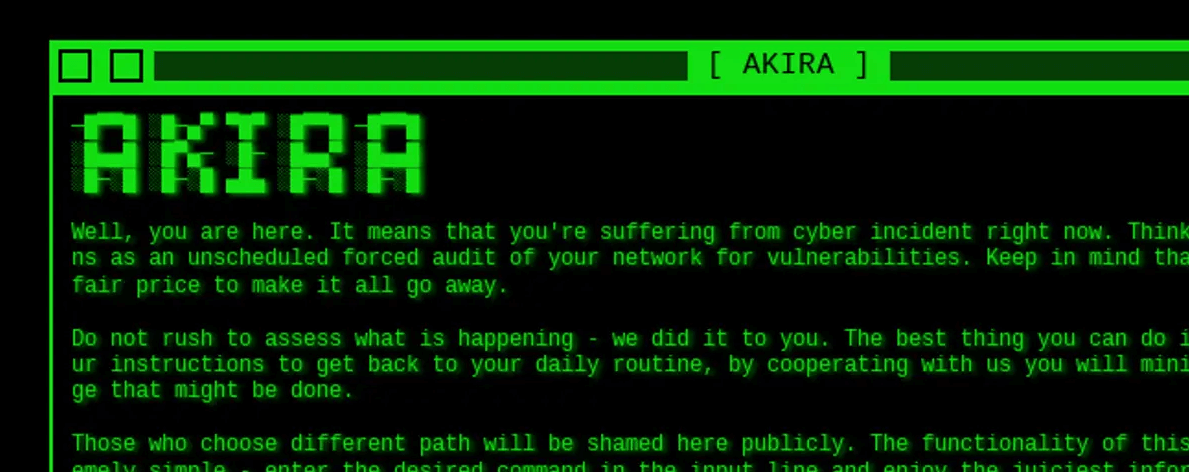
Akira
First spotted around April 2023, Akira ransomware appears to be one of the better-organised criminal efforts to extract payments from victims.
Suitable for multiple operating systems and sporting a green-and-black ransom note aesthetic Sophos describes as ‘Retro’, Akira is a professional effort that should give pause for thought.
Disabling many security settings to give itself more lateral movement on systems, the infection also tries to destroy backups to hinder the user, and has a ransom note written in (relatively) good quality English with a host of supporting infrastructure to help the hacker leverage a bigger payout.
The threat actor(s) behind Akira were known to exploit an existing VPN vulnerability to spread the ransomware, but had used stolen credentials purchased online from third-party data breaches to get started – in what has become a common pattern of low level breaches by third-parties supplying the more serious cyber crime via online black markets.
MedusaLocker
Originating back in 2019, this nasty ransomware has been through a string of variants with the most recent strain popping up in September 2023 to hit a major European health organisation.
MedusaLocker is an example of ‘Ransomware-as-a-Service’ – anybody can purchase and launch their own version, with a typical ransom being around $12,000. Like legal software companies, the developers behind Medusa even offer their customers a Support Helpdesk!
More recent variants have moved over to ‘double-extortion’ style attacks, where the hacker not only compromises the data, but threatens to leak a copy online, which is more likely to compel healthcare and public-sector organisations holding very private information on behalf of the public to pay the ransom demand.
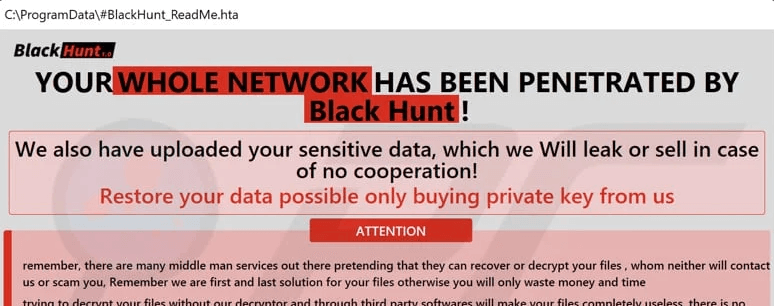
Black Hunt
Targeting Windows environments, this ransomware looks relatively traditional, but may show the shape of things to come.
It can be spread both by email and via drive-by downloads on malicious websites that purport to give away free software or content, and for a special trick, immediately tries to terminate other processes on the user’s machine to speed up how quickly it can corrupt data – getting ahead of efforts to slow it down.
Curiously the ransomware searches for a specific text file called ‘Vaccine.txt’, which is likely a safety mechanism used by the original developers to protect their own systems against the dangerous infection.
The Group behind Black Hunt also use a tactic becoming increasingly popular among cyber criminals – publicly naming their victims in a perverse online ‘Hall of Fame’ – as a warning to others.
Our Verdict:
Keeping your data, staff and systems safe from ever-evolving ransomware infections means instilling good cyber-hygiene among your organisation, backed by a cyber security strategy that covers a range of areas including; endpoint protection, identify security, perimeter defence and user awareness training among others. Learn more here.
For Cyber Security Expertise and Support, please contact our team today.